- 128.00 KB
- 2021-05-13 发布
- 1、本文档由用户上传,淘文库整理发布,可阅读全部内容。
- 2、本文档内容版权归属内容提供方,所产生的收益全部归内容提供方所有。如果您对本文有版权争议,请立即联系网站客服。
- 3、本文档由用户上传,本站不保证质量和数量令人满意,可能有诸多瑕疵,付费之前,请仔细阅读内容确认后进行付费下载。
- 网站客服QQ:403074932
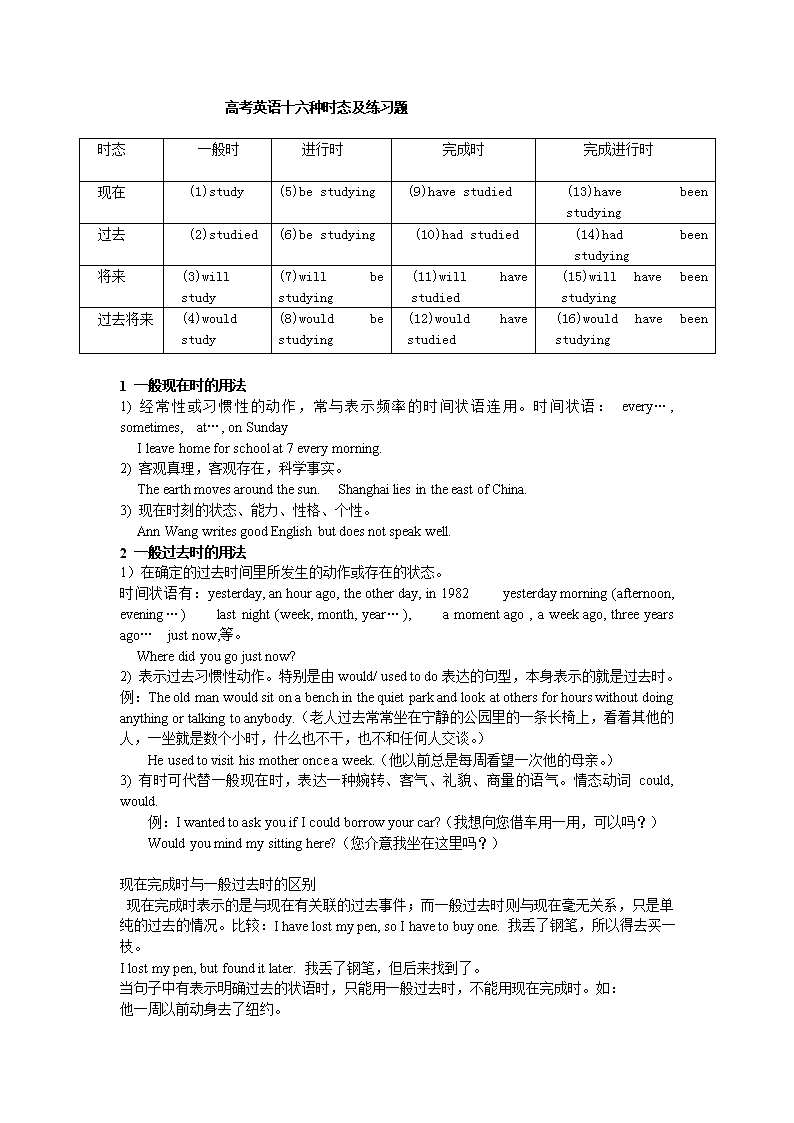
高考英语十六种时态及练习题
时态
一般时
进行时
完成时
完成进行时
现在
(1)study
(5)be studying
(9)have studied
(13)have been studying
过去
(2)studied
(6)be studying
(10)had studied
(14)had been studying
将来
(3)will study
(7)will be studying
(11)will have studied
(15)will have been studying
过去将来
(4)would study
(8)would be studying
(12)would have studied
(16)would have been studying
1 一般现在时的用法
1) 经常性或习惯性的动作,常与表示频率的时间状语连用。时间状语: every…, sometimes, at…, on Sunday
I leave home for school at 7 every morning.
2) 客观真理,客观存在,科学事实。
The earth moves around the sun. Shanghai lies in the east of China.
3) 现在时刻的状态、能力、性格、个性。
Ann Wang writes good English but does not speak well.
2 一般过去时的用法
1)在确定的过去时间里所发生的动作或存在的状态。
时间状语有:yesterday, an hour ago, the other day, in 1982 yesterday morning (afternoon, evening…) last night (week, month, year…), a moment ago , a week ago, three years ago… just now,等。
Where did you go just now?
2) 表示过去习惯性动作。特别是由would/ used to do表达的句型,本身表示的就是过去时。
例:The old man would sit on a bench in the quiet park and look at others for hours without doing anything or talking to anybody.(老人过去常常坐在宁静的公园里的一条长椅上,看着其他的人,一坐就是数个小时,什么也不干,也不和任何人交谈。)
He used to visit his mother once a week.(他以前总是每周看望一次他的母亲。)
3) 有时可代替一般现在时,表达一种婉转、客气、礼貌、商量的语气。情态动词 could, would.
例:I wanted to ask you if I could borrow your car?(我想向您借车用一用,可以吗?)
Would you mind my sitting here?(您介意我坐在这里吗?)
现在完成时与一般过去时的区别
现在完成时表示的是与现在有关联的过去事件;而一般过去时则与现在毫无关系,只是单纯的过去的情况。比较:I have lost my pen, so I have to buy one. 我丢了钢笔,所以得去买一枝。
I lost my pen, but found it later. 我丢了钢笔,但后来找到了。
当句子中有表示明确过去的状语时,只能用一般过去时,不能用现在完成时。如:
他一周以前动身去了纽约。
误:He has left for New York a week ago. 正:He left for New York a week ago.
另外,当句首为疑问词when时,其后可用一般过去时,不能用现在完成时。如:
你什么时候和他首次见面的?
误:When have you first met him? 正 :When did you first meet him?
3一般将来时
一、意义:表示将来某个时间要发生的动作或存在的状态,也表示将来经常或重复发生的动作。
时间标志:tomorrow , soon , next Monday , next year , next weekend , this afternoon , this evening ……
二. 构成及变化:
一般将来时常用的两种结构
be going to+动词原形 : 表示打算、准备做的事或即将发生或肯定要发生的事。
shall/will+动词原形 : 表示将要发生的动作或情况,没有太多的计划性, 还用来表示意愿
He’s going to New York next week.下周他要去纽约.
It will rain tonight.
一般现在时表将来
1)下列动词:come, go, arrive, leave, start, begin, return的一般现在时表将来。这主要用来表示在时间上已确定或安排好的事情。
The train leaves at six tomorrow morning.
When does the bus star? It stars in ten minutes.
2)倒装句,表示动作正在进行,如:
Here comes the bus. = The bus is coming.
There goes the bell. = The bell is ringing.
3)在时间或条件句中。
When Bill comes (不是will come), ask him to wait for me.
I'll write to you as soon as I arrive there.
4)在动词hope, take care that, make sure that等后。
I hope they have a nice time next week.
Make sure that the windows are closed before you leave the room.
4.过去将来时(would do)
概念:立足于过去某一时刻,从过去看将来,常用于宾语从句中。
时间状语:the next day(morning, year…),the following month(week…),etc.
(一)“would+动词原形”。常表示按计划或安排即将发生的事。例如
He said he would come to see me.
他说他要来看我。
He told me he would go to Beijing.
他告诉我他将去北京。
(二)“was/ were+going to+动词原形”。常可用来表示按计划或安排即将发生的事。例如:
She said she was going to start off at once.
她说她将立即出发。
I was told that he was going to return home.
有人告诉我他准备回家。
此结构还可表示根据当时情况判断有可能但不一定会发生某事。例如:
It seemed as if it was going to rain.
看来好像要下雨。
(三)come, go, leave, arrive, start等动词可用过去进行时代替过去将来时。例如:
He said the train was leaving at six the next morning.
他说火车将于第二天早晨六点离开。
She told me she was coming to see me.
她告诉我她要来看我。
1- The plane is leaving right now, but Jim hasn't arrived yet.
- Well, he said he _____here on time.
A came B would come C can be D will be
2 As soon as the baby saw her mother, she _____.
A was going to cry B cried C began to cry D was crying
3 Li Ming said he _____happy if Brian_____to China next month.
A as; come B was; would come C would be; came D will be; come
4Jenny said she _____her holiday in China.
A spent B would spent C was going to spent D would spend
5现在进行时( be doing)
1)表示现在( 指说话人说话时) 正在发生的事情。
We are waiting for you.
2)习惯进行:表示长期的或重复性的动作,说话时动作未必正在进行。
Mr. Green is writing another novel.
(说话时并未在写,只处于写作的状态。)
3)表示计划或安排好了的将来动作,常与一个表示将来的时间状语连用
Mike is coming home on Thursday. 迈克星期四回来
一般现在时与现在进行时的区别
(一) 一般现在时表示动作的习惯性和经常性,可带频率时间,无时限性。现在进行时表示动作的暂时性;
The shop closes at 7:30 p.m. Father doesn’t smoke. (习惯)
I watch TV every day. (经常性) I am watching TV now. (暂时性)
He studies hard. 他(经常)努力学习。 He is studying hard. 他(此刻或现阶段)正在努力学习。
(二)持续动词的一般时表持续情况,表示长久性动作,经常性,习惯性行为或客观存在的事实、事物的本质特性,没有时限性。进行时表暂时性或有限时刻的持续,表示短暂性动作,
The table ____ soft。(feels) 表特性特征。 Japan ___ in the east of China。(lives) 表客观事实
He lives in Beijing.(生活在北京- ) He is living in Beijing.(目前住在北京暂时性)
Lucy lives in Beijing. (长久性居住) Lucy is living in Beijing.(短时间居住)
短暂动词的一般时叙述事实,特征,能力,而进行时描述反复发生,即将发生或刚开始行为。
He jumps high. (特征) He is jumping very high. (反复)
考题1 I don’t really work here! I ___ until the new secretary arrives.
A. just help out B. Have just helped out C.am just helping out D. Will just help out 分析 依题意“我不能在此工作”,说明help out这一行为只是眼前暂时发生的事,选C。
考题2 It seldom ___ her but it ____ heavily.
A. snows/snows B.snows /snowing C. Is snowing /I s snowing D. Is snowing /snows
分析 seldom 表频率叙述经常性事实用一般现在时,but 转折描述眼前暂时情况,用现在进行时,故选B。
(三)现在进行时带always,continually,forever,constantly, for ever等频率副词,表示重复的动作,有着极大的感情色彩,表示不满或满意。,而一般现在时所表述的动作通常是事实。
You’re always forgetting the most important things. (责备) He often helps others. (事实)
He is always making noises in class. (讨厌) He is always helping others. (赞扬)
He is perpetually interfering in my affairs.她老是干预我的事。 (不满)
The students are making progress constantly.学生们在不断进步。 (满意)
(四)一些表示情感状态、知觉认识、愿望或短暂性的动词,不能用进行时,不能用现在进行时态,通常用一般现在时表示说话时发生的动作而应用一般现在时。如:see(明白),hear,know(知道),understand,want(需要;想要),like(喜欢),love,like,hate, wish,hope,believe,hear,have(有),think(想;认为),agree, notice,等等。
I have a lot of friends here.
严格区分进行时与一般时的语义
(五)come,go,leave,start,return,move,reach,sail,fall 等一般时态表客观规定计划,进行时表主观打算推测。
Flight 254 leaves at 5:30. (表客观规定计划) The plane is taking off an hour later.(主观判断)
(六)一般现在时表示现在发生的动作,现在进行时表示眼前看得见的动作。例如:
Boats pass under the bridge. 船从桥下穿过。The boat is passing under the bridge.船正从桥下穿过。
6 过去进行时(was/were doing)
1)概念:过去进行时主要表示过去某一时刻正在进行的动作,或表示过去某一阶段一直在进行的动作
2)过去进行时的主要用法是描述一件事发生的背景;一个长动作发生的时候,另一个短动作发生。
3) 常用的时间状语
this morning, the whole morning, all day yesterday, from nine to ten last evening, when, while
It was raining when they left the station.
When I got to the top of the mountain, the sun was shining.
典型例题
1) Mary ___ a dress when she cut her finger.
A. made B. is making C. was making D. makes
2) As she ___ the newspaper, Granny ___ asleep.
read; was falling B. was reading; fell C. was reading; was falling D. read;fell
一、过去进行时结构:
was/were + 动词的现在分词
否定句则在was/were后加一个not,疑问句将was/were提前则可。
如:He was reading a book at 5:00pm yesterday.
→He was not reading a book at 5:00 yesterday.
→Was he reading a book at 5:00 yesterday? (Yes, he was./ No, he wasn’t.)
→What was he doing at 5:00 yesterday?
二、过去进行时用法:
1. 过去进行时主要表示过去某个时刻正在进行的动作,常和表示过去的状语连用。如:
(just)then 那时,当时 at this/that time 在这/那时 yesterday afternoon昨天下午
at nine 在九点 last night 昨晚 (at)this time yesterday在昨天这个时候
但在不少情况下,没有表示时间的状语,这时需要通过上下文来表示。
①What were you doing at nine last night? 昨晚九点的时候,你在做什么?
②I was watching TV at home yesterday afternoon. 我昨天下午正在家里看电视。
③They were playing football at this time yesterday.昨天这个时候他们在踢足球。
2.过去进行时也可以表示过去某一段时间内正在进行的动作。常与those days, the whole morning, from 8:00 to 12:00 last night等时间状语连用。
(1)From 1983 to 1998 , he was teaching at Yale . 从1983到1998年,他正在耶鲁大学教书。
(2)They were building a bridge last winter . 去年冬天他们正在造一座桥。
(3) He was writing a book those days. 那几天他正在写一本书
3、过去进行时和一般过去时的区别。
(1)过去进行时表示过去某时正在进行的动作,而一般过去时则表示一个完成的动作。也就是说用一般过去时,只表示有过这件事;用过去进行时,则强调动作的连续性。
① I wrote a letter this morning. 今天上午我写了一封信。(信写完了)
I was writing a letter this morning. 今天上午我在写一封信。(信不一定写完)
(2) 表示过去的状态、感觉及心理活动的静态动词(如be, like, love, hate, fear, own, hear, see, know, want, notice)可用于一般过去时,但通常不用于进行时。如:
I hated it when a man spoke with his mouth full of food. 我讨厌人们说话时口里含着食物。
下面几种情况不用一般过去时而要用过去进行时:
(1) when作并列连词,表示“(这时)突然”之意时,第一个并列分句用过去进行时,when引导的并列分句用一般过去时。如:
I was taking a walk when I met him. 我正在散步,突然遇见了他。
We were playing outside when it began to rain. 我们正在外边玩,这时下起雨来了。
(2) go, come, leave, start, arrive等动词可用过去进行时表示过去将来的含义。如:
I was leaving for Wuhan that day. 那天我正要去武汉。
She was coming later. 她随后就来。
过去进行时巩固练习:
1. Simon _____________ (make) a model plane at 8:00 a.m.
2. Peter ______________(do) his homework at seven last night.
3. They ____________ (watch) a football match from 7:00 to 9:00 last night.
4. He _____________(try) to draw a plane on the blackboard at that time.
5. What book ________ you ____________(read) when I ________ (see)you at four yesterday afternoon?
6. While she __________ (watch) TV, her son ____________ (play) outside the room.
7. It ________ (begin) to rain when we _____________(work) in the field.
1. I ________ (do) my homework last night when the light _______ (go) out. {go out 意为熄灭}
2. ——I saw you in the reading room yesterday , Tom. What were you doing?
------Oh, I ____________ (read) some books on science.
10.--- Did you see Tim just now?
--- Yes. He __________ (fish) by the river.
11.When the teacher ______ (come) into the classroom, the students __________(laugh)loudly.
7将来进行时(shall/will be doing)
将来某时(段)正进行,预计不久要发生。通常用在口语中,语气委婉顿生情。”
【用法】 将来进行时由“助动词will / shall + be + 现在分词”构成,具体用法如下:
(1) 表示将来某时刻或某段时间正在进行的动作。常与soon, tomorrow, this evening, on Sunday, by this time, in two days, tomorrow evening等表示将来的时间状语连用。如:
I will be having an English class at 8 tomorrow. 我明天八点钟正在上英语课。
Mary will be working in the factory in the next two months.下两个月玛丽将在这个厂里工作。
(2) 在口语中常用来表示按计划或安排即要发生的动作。如:
This time tomorrow I shall be flying to New York. 明天这个时候我将飞往纽约。 At 7:00 this evening I will be watching the news programmes on TV. 今晚七时,我将正在收看电视上的新闻节目。
(3) 表示预料不久要发生或势必要发生的事情或将来的某种可能性,说话人往往有“我料想”或“我估计”的含义。如:
We believe that peasants’ life will be getting better and better. 我们相信农民的生活会越来越好。
If we don’t do so, we shall be making a serious mistake. 如果我们不那样做,我们就会犯严重的错误。 (4) 表示亲切或委婉的语气。如:
When shall we be meeting again? 我们什么时候再见面?
【注意】在时间、条件等状语从句中,用现在进行时代替将来进行时。如: Be careful when you are crossing the street. 过马路时要当心。
If Tom is doing his homework when you come back, don’t disturb him, please. 你回来时如果汤姆正在做作业,请不要打扰他。
8过去将来进行时(should/would be done)
一. 基本结构:
1.过去将来进行时由should(would)+be+现在分词
2.否定:should(would)+not
二. 基本用法:
1.过去将来进行时表示就过去某一时间而言,将来某一时刻或某一段时间正在进行的动作,主要用于宾语从句 中,尤其多用于间接引语中。
举例:
They said they would be coming. 他们说了他们将要来。 (用于间接引语中)
He asked me what I should be doing at six the next day. 他问我次日六点将正在做什么。 (用于间接引语中)
The new job he would be taking was raising racing horses. 他将要接受的新工作是养赛马。 (用于定语从句中)
2.过去将来进行时可以表示在过去某一时间之后即将进行的动作。
举例:
He said he could not come because he would be having a meeting. 他说他不能来因为要开会。
3.过去将来进行时表示在过去将来某一时间正在发生的动作。它常和表示过去将来的时间状语连用, 但上下文清楚时,时间状语亦可省略。和将来进行时一样,它也常表计划中的事,不表意愿或打算。它还有一个特点,即常用在宾语从句(尤其是间接引语)中。 举例:
John told us that Mary would be coming next day. 约翰告诉我们玛丽第二天来。
I never realized that some day I would be living in China. 我从未想到将来有一天会在中国居住。
She said she would be setting off on the 10 o’clock train. 她说她将乘10点钟的火车走。
4.过去将来进行时有时也可用在其它从句中。
举例:
The new name he would be using was Jack Jones. 他将用的新名是杰克·琼斯。(用在定语从句中)
He would pay the rest as he would be leaving France.
其余款项,他将在离开法国时付清。(用在状语从句中)
5.过去将来进行时也可用在独立句中。
The car started. Ellen James would be driving off to the university.
车子发动了。埃伦·詹姆斯要开车到大学去。
9现在完成时 (have/has done)
表示到说话时为止(或到现在为止)已经发生或完成了(不一定结束)的动作或状态。过去某一时间开始并一直持续到现在并且有可能还会持续的动作或状态。
现在完成时用来表示之前已发生或完成的动作或状态,其结果的确和现在有联系。动作或状态发生在过去但它的影响现在还存在;也可表示持续到现在的动作或状态。
四种用法
表示影响
表示一个过去发生的动作在过去已经完成,并且这个过去发生并完成的动作对现在有影响或结果,同时说话者强调的或感兴趣的就是这个影响或结果,如汉语说“他已离开这个城市了”,其中的“离开”肯定发生了,它对现在的影响或结果就是“他现在已不在这个城市了”;又如汉语说“有人把窗户打破了”,显然“打破窗户”这一动作发生在过去,并且在过去已经完成了,但说话人强调的重点是打破窗户对现在的影响——窗户现在仍是破的。如:
He has been away from the city.他已离开这个城市。(结果:他不在这个城市。)
Someone has broken the window.有人把窗户打破了。(结果:窗户仍破着。)
I have lost my pen. 我把钢笔丢了。根据句意可知,“丢钢笔”这个动作发生在过去,同时也在过去已经完成,但这个过过去发生和完成的动作对现在有影响——我现在无钢笔用,或我得去买支新的。
We have finished the work. 我们已把工作干完了。显然“完成工作”这个动作发生在过去,同时也在过去已经完成,但这个过过去发生和完成的动作对现在有影响——我们可以休息了,或可以回家了,或可以做别的事了。
表示持续
表示一个过去发生的动作或开始的状态在过去并未完成或结束,而是一直持续到现在,并且有可能继续下去(也可能到此结束),如汉语说“他在我们学校教书已有30年了”,显然“他在我们学校教书”是从30年前开始,并且一直教到现在,已经持续了30年;又如汉语说“自上个星期以来他一直很忙”,显然“忙”是从上个星期开始的,并且这一“忙”就一直忙到现在。如:
I’ve waited a week for your answer. 等你的答复我已等了一个星期。
根据句意可知,“等”这个动作发生在过去,但它在过去并没有完成,而是一直等到现在,已持续了一个星期。
We have lived here quite a number of years. 我们在这里住了很多年了。
根据句意可知,“住在这儿”是从过去开始的,但它在过去并没有完成,而是一直等到现在,已持续了好几年。
表示重复
即表示从过去某个时间直到现在的这个时间范围内不断重复发生的动作或情况,并且这个不断重复的动作有可能继续下去,也有可能到现在就结束。如:
How often have you seen her again? 你隔多长时间见她一次?
My father has always gone to work by bike. 我父亲一向骑车上班。
表示将来
同一般现在时可以表示将来一样,现在完成时也可以在时间状语从句里表示将来。如:
I’ll wait until he has written his letter.我愿等到他把信写完。
When you have rested, I’ll show you the garden.等你休息好之后,我领你看我们的花园。典型例题
(1) ---Do you know our town at all?
---No, this is the first time I ___ here.
A. was B. have been C. came D. am coming
(2) ---Have you ____ been to our town before?
---No, it's the first time I ___ here.
A. even, come B. even, have come C. ever, come D. ever, have come
现在完成时与一般过去时的区别
一般过去时表示动作对现在没有影响,用现在完成时则表示动词对现在影响。你对这样的解释肯定不满意,因为你认为过去发生的动作不管你用什么时态,它对现在的影响都是存在的,并不会因为你所用的时态不同而有所变化。比如你过去记的单词对你现在有影响,你过去搞的锻炼对你现在有影响,你过去看的电影对你现在有影响,你过去犯的错误对你现在有影响,你过去缺过课对你现在有影响,等等。
其实,对于过去发生并已完成的动作,不管你是用一般过去时还是用过去完成时,它对现在都是有影响的,它们的不同之处在于,说话者是否强调这个影响——如果强调对现在的影响,就用现在完成时;如果不强调对现在的影响,而是强调动作发生的过去时间,就用一般过去时。体会下面的句子(注意体会说话者用现在完成时的言外之意):
例一
I’ve washed the car. 我已经洗过车了。 I washed the car. 我洗了车子。
第一句用的是现在完成时,它强调的是洗车对现在的影响——车现在是干净的,你若原计划去洗车的现在就无需去洗了,等等(这就是说话者用现在完成时的言外之意);第二句用的是一般过去时,它不强调洗车对现在的影响,只表明车在过去洗过,至于它现在是否干净说话人并不关心。
例二
The lift has broken down. 电梯坏了。 The lift broke down. 电梯坏了。
第一句用的是现在完成时,它强调的是电梯坏对现在的影响——我们不得不走楼梯,或我们得请人来修电梯,等等(这就是说话者用现在完成时的言外之意);第二句用的是一般过去时,它不强调电梯坏对现在的影响,只表明电梯在过去曾经坏过,至于它现在是否能用说话人并不关心。
例三
Tom has had a bad car crash. 汤姆发生了严重的车祸。(他可能仍在住院。)
Tom had a bad crash. 汤姆发生过严重车祸。(他现在很可能已经出院了。)
第一句用的是现在完成时,它强调的是出车祸对现在的影响——汤姆可能现在仍在住院,可能无法现在就去参加某项活动,等等(这就是说话者用现在完成时的言外之意)第二句用的是一般过去时,它不强调出车祸对现在的影响,只表明汤姆在过去曾经出过车祸,至于他现在是否已经出院之类的相关说话人并不关心。
如何理解现在完成时强调影响?
1. 现在完成时,强调过去的动作对现在的影响。就是说,动作发生在过去,然而该动作的结果对现在有影响。
Tom has eaten something. 汤姆吃了一些东西。(意味着:He is not hungry now. 他现在不饿了。)
My daughter has already phoned me about her health. 我女儿已经给我来电话,说过她身体情况。(意味着:So I am not worried about her. 于是我不担心她了。)
I haven’t heard from my friend John. 我一直没有朋友约翰的消息。(意味着:I don’t know how he is getting along.)
以上各个例句,假若使用一般过去式,也完全正确。但无法表达那种对现在的影响或结果。
2. 表示过去的某一动作或状态一直持续到现在,并有可能持续下去。
We have studied English for seven years. 我们已经学了七年英语。
His uncle has worked in this factory since he left the army. 他叔叔自从离开部队以来一直在这家工厂上班。
She’s been very busy lately. 她最近非常忙。
【用法辨析】现在完成时与一般过去时的用法区别
这两个时态都可以指过去已发生的事,但现在完成时强调动作与现在有联系,或是对现在有影响;而一般过去时单纯谈过去的事情,与现在没有联系。凡是有明确的过去时间状语时,只能用一般过去时。
The prices have gone down,but I wonder if they’ll remain so. 价格已经降下来了,但我不知是否会继续保持这样。(现在仍低)
The prices went down for a long time last year. 去年价格曾下降过一段很长的时间。(现在已经回升)
Now he’s a worker,and he once served in the army for 5 years.他现在是个工人,他曾在部队服过5年兵役。(现在已离开部队)
He has served in the army for 5 years. 他当兵5年了。(现在还在部队)
【特别注意】在现代英语中,尤其美国英语中,常用一般过去时代替现在完成时,不太考虑过去动作对现在的影响与否。
I saw the film already. (= I have seen the film already.) 我看过这部电影。
10 过去完成时(had done)
1.概念:以过去某个时间为标准,在此以前发生的动作或行为,或在过去某动作之前完成的行为,即“过去的过去”。
2.时间状语:before, by the end of last year(term, month…),etc.
3.基本结构:had + done.
4.否定形式:had + not + done.
5.一般疑问句:had放于句首。
6.例句:As soon as we got to the station, the train had left.
By the end of last month. We had reviewed four books
2) 用法
a. 在told, said, knew, heard, thought等动词后的宾语从句。
She said (that) she had never been to Paris.
b. 状语从句
在过去不同时间发生的两个动作中,发生在先,用过去完成时;发生在后,用一般过去时。
When the police arrived, the thieves had run away.
c. 表示意向的动词,如hope, wish, expect, think, intend, mean, suppose等,用过去完成时表示"原本…,未能…"
We had hoped that you would come, but you didn't.
3) 过去完成时的时间状语before, by, until , when, after, once, as soon as。
He said that he had learned some English before.
By the time he was twelve, Edison had began to make a living by himself.
Tom was disappointed that most of the guests had left when he arrived at the party.
典型例题
The students ___ busily when Miss Brown went to get a book she ___ in the office.
A. had written, left B,were writing, has left C. had written, had left D. were writing, had left
注意: had no … when 还没等…… 就……
had no sooner… than 刚…… 就……
He had no sooner bought the car than he sold it.
过去完成时与一般过去时的区别
从用法上说,一般过去时表示过去某时发生的动作或存在的状态,而过去完成时则表示过去某一时间以前(即过去的过去)发生的动作或存在的状态。但有时某个动作虽然发生在“过去的过去”,但却也可用一般过去时,如:
(1) 当几个过去的动作用and, then, but等连接,且按照动作发生的先后顺序表达时,几个动作均可用一般过去:
I bought a radio but lost it. 我买了一部收音机,但丢了。
Very soon she apologized and left. 不久她表示了歉意就走了。
He retired and wrote his memoirs. 他退休了,撰写了他的回忆录。
He stood up, took his coat and went out. 他站起身来,拿起外套,然后就出去了。
The little girl alternately sulked and made scenes. 这小姑娘一会儿生闷气,一会儿和人吵架。
(2) 由after, before, as soon as 等连词引导时间状语从句,由于这些连词已经清楚地表明了主从句谓语动词的先后顺序,所以对于先发生的动作也可用一般过去时表示:
I told them the news after you (had) left. 你走后我把这消息告诉了他们。
As soon as I (had) put the phone down it rang again. 我刚把电话一放下,它又响了。
(3) 在一定的语境中,表示过去未曾实现想法或打算的过去完成时也可用一般过去时表示:
He hoped to come with us, but he was too busy. 他本想同我们一起来的,但他太忙了。
I thought I could go, but I can’t. 我原认为我能去,但我(现在)去不了。
【注】若没有明确的语境,则宜用过去完成时表示过去未曾实现的想法,否则可能有歧义,如说I hoped to pass the examination. 它只表明过去想通过考试,但并未说明通过与否。如说 I had hoped to pass the examination,则表示过去想通过考试,但实际上未通过。不过在过去式后接不定式的完成式也可明确表示过去未曾实现的想法,如 I hoped to have passed the examination。
过去完成时与现在完成时的区别
现在完成时表示的动作发生在过去,以现在的时间为基点,但侧重对现 在产生的结果或造成的影响,与现 在有关,其结构为“助动词have (has) + 过去分词”;过去完成时则是一个相对的时态,以过去时间为基点,它所表示的动作不仅发生在过去,更强调“过去的过去”,只有和过去某时或某动作相比较时,才用到它。
比较:I have learned 1000 English words so far.到目前为止我已经学会了 1000 个英语单词。
I had learned 1000 English words till then.到那时为止我已经学会了 1000 个英语单词。
— I'm sorry to keep you waiting. 对不起,让你久等了。
— Oh, not at all. I have been here only a few minutes.没什么,我只等了几分钟。(“等”的动作从过去某一时间点持续到现在)
过去完成时与现在完成时都跟表示一段时间的状语连用,如:for a week,for two years,for a long time等,但现在完成时表示的,是延续到现在或同现在有关的动作(句中不能有明确表示过去时间的状语),而过去完成时表示的,是在过去某时间之前已经完成或延续到过去某时间的动作(句中有表示过去某特定时间的状语)。如:
① She had been ill for a week before she came back. 她在回来之前就病一个星期了。(到过去某时间)
② She has been ill for a week. 她生病一个星期了。(到现在仍生病)
②Everything had gone well up to that time.直到那时,一切都很顺利。(到过去某时间)
Everything has gone well up to now.直到现在,一切都很顺利。(到现在为止
过去完成时与一般过去时的区别
虽然这两种时态都表示过去发生的动作或存在的状态,但在使用时应注意以下几点:
1. 时间状语不同:过去完成时在时间上强调“过去的过去”;而一般过去时只强调过去某一特定的时间。
比较:They had arrived at the station by ten yesterday.
They arrived at the station at ten yesterday.
2. 在没有明确的过去时间状语作标志时,谓语动词动作发生的时间先后须依据上下文来判断:先发生的用过去完成时,后发生的则用一般过去时。
She was very happy. Her whole family were pleased with her, too. She had just won the first in the composition competition.
3. 当两个或两个以上接连发生的动作用 and 或 but 连接时,按时间顺序,只需用一般过去时来代替过去完成时;另外,在 before , after , as soon as 引导的从句中,由于这些连词本身已经表示出时间的先后,因此也可以用过去时来代替过去完成时。
He entered the room, turned on the light and read an evening paper.
过去完成时表示过去的过去,不单独使用,一般和一般过去式一起使用。
11将来完成时(shall/will have done)
将来完成时用来表示在将来某一时间以前已经完成或一直持续的动作经常与before+将来时间或by+将来时间连用,也可与before或by the time引导的现在时的从句连用。
将来完成时的构成是由"shall/will + have +过去分词"构成的。
Before long he will have forgotten all about the matter.
不久他就会全然忘记这件事的。
他现在是一个有身份的人了,他可能不会记得老同学了。
Will you have known Kevin for 10 years next month?
到下个月你认识凯文该有10年了吧?
用法:
1表示在将来某一时间之前已完成的动作,并往往对将来某一时间产生影响。
We shall have learned 12 units by the end of this term.
到这个学期末,我们将学完12个单元。
By the time you get home I will have cleaned the house from top to bottom.
你到家之前我将把房子彻底打扫一遍。
2表示推测,相当于"must have done"结构。
You will have heard of this, I guess.
我想你已经听说过这件事了。
I am sure he will have got the information.
我相信他一定得到了这个信息
3 将来完成时通常与:“by+将来时间”和"by the time that"结构连用
例如:
① By the year 2050, scientists probably will have discovered a cure for cancer.
到2050年,科学家们可能已经找到了治愈癌症的方法。
② By the time you arrive in London, we will have been staying in Europe for two weeks.
等你到达伦敦的时候,我们已经在欧洲呆了两星期了。
4. 在时间从句和条件从句中,现在完成时可以代替将来完成时,表示将来某时业已完成的动作
例如:
① You'll get to like the subject after you have studied it for some time.
在学习这个学科一段时间之后,你就会喜欢它的。
② I'll go and see the exhibition as soon as I have finished my work.
我一做完作业就去看展览。
5. 将来完成时还可以表示“可能性”,或“设想”
例如:
It's five o'clock, they will have arrived home by now.
已经五点钟了,他们现在应该已经到家了
现在完成时、过去完成时与将来完成的区别
现在完成时以现在时间为参照点,表示在“现在”以前完成的动作或持续到“现在”的状态,过去完成时则以过去时间为参照点,表示在“过去”某一时间以前发生的动作或持续到“过去”某一时间的状态,将来完成时则以将来时间为参照点,表示在“将来”某一时间为止已经完成的动作或持续到“将来”某一时间的状态:
He has finished writing his novel. 他已写完了他的小说。
He had finished writing his novel by the end of last year. 去年年底他就写完他的小说。
He will have finished writing his novel by the end of next year. 到明年年底他就会写完他的小说了。
与一般现在时代替一般将来时一样,在表示时间或者条件的状语从句,通常要用现在完成时来表示将来完成时,而不能直接使用将来完成时:
I will go with you when I have finished my work. 等我完成工作之后我就同你去。
若不强调动作的完成(且不致于引起歧义),有时也可用一般现在时:
I will go with you when I finish my work. 我完成工作后就同你去。
将来完成时专项练习
1. By the end of this year ,I ____enough money for a holiday
A will save B will be saving C will have saved Dhave saved
选C,by the end of this year, 是明确表示将来的时间状语,主句表示在这个将来时间以前完成的动作,故应用将来完成时.
2.When i have done that,I (______) all I was supposed to do.(do)
我做完了这件事,就做完了我全部应该做的事情。Will have done
A improves B improved C will be improved D will have improve
选D,by the time 引出的是时间状语分句,分句中用的come用一般现在时,表示将来概念,相当于一个表示将来的时间状语,主句谓语动词表示在将来某一时刻以前必定完成的行为,应该用将来完成时.不能选A,句子中带有表示将来时间的状语分句,故应该用与将来时相关的时态.也不能选C ,improve 在该句中作”好转”,”变得更好”解,为不及物动词,所以用被动语态时错误的.
A had finished B will have finished C would have finished D finished
B
5. I suppose by the time I come back in ten years’ time all these old house______down.( )
A will have been pulled B will be pulling C will have pulled D will be pulled
A
6. I hope that they ______the road by the time we come back.
A will have repaired B would have repaired C have repaired D had repaired
A
12过去将来完成时(would have done)
用法及用例
过去将来完成时表示在过去看来将来某时会已经完成的动作:
She said she’d have finished her exams by then. 她说那时她会已经考完试了。 I thought Sophia would have told you something. 我想索菲娅会已告诉你一地情况。 I thought you would have finished by now. 我想你现在一定已经干完了。
There are a lot of things I should have liked to ask you. 有好些事我本想问你的。 He knew by the time he arrived she would have gone home. 他知道他到时她会已经回家了。
Well, well! Who would have guessed it! 真是的! 这谁会想到呀!
13. 现在完成进行时(have been doing)
1.现在完成进行时表示某动作从过去某个时间开始,一直延续到现在,并且还有可能持续下去。如:
We have been waiting for him for two hours. 我们等他等了两个小时。
2.现在完成进行时的用法
现在完成进行时由“have /has been + 现在分词”构成。
3.现在完成进行时所用的时间状语:this month / week / year, these days, recently / lately, in the past few + 时间段, since +时间点, for + 时间段。如:
They have been building the bridge for two month. 两个月来他们一直在修桥。
They have been planting trees this month. 这个月来他们一直在植树。
4. 现在完成进行时与现在完成时的区别
(1) 现在完成时强调动作的完成,而现在完成进行时强调动作的延续,因此,表示动作的完成,只能用现在完成时,而不能用现在完成进行时。如:
He has changed his idea. 他改变了想法。
(2) 在表示动作的延续时,虽然既可用现在完成时,也可用现在完成进行时,但现在完成进行时强调动作的进行。因此在需要明确表示动作还要持续下去时,应用现在完成进行时。如:We have been studying here for two years. 我们在这儿已经学习了两年了。
(3) 有些延续性动词(如 keep, learn, live, stay, study, work等),用于现在完成时或现在完成进行时的区别不大。如:I have lived here for many years.=I have been living here for many years. 我在这儿住了多年了。
现在完成进行时的谓语动词构成
(一)表示从过去某时开始一直持续到现在的动作,并且还将持续下去。
The Chinese have been making paper for two thousand years.
中国有2000年的造纸历史。(动作还将继续下去)
I have been learning English since three years ago.
自从三年前以来我一直在学英语。(动作还将继续下去)
(二)表示在说话时刻之前到现在正在进行的动作。
We have been waiting for you for half an hour.
我们已经等你半个钟头了(人还没到,如同在电话里说的,还会继续等)
(三)有些现在完成进行时的句子等同于现在完成时的句子。
They have been living in this city for ten years.
They have lived in this city for ten years.
他们在这个城市已经住了10年了。
I have been working here for five years.
I have worked here for five years.
我在这里已经工作五年了。
(四)大多数现在完成进行时的句子不等同于现在完成时的句子。
I have been writing a book.(动作还将继续下去) 我一直在写一本书。
I have written a book.(动作已经完成) 我已经写了一本书。
They have been building a bridge. 他们一直在造一座桥。
They have built a bridge. 他们造了一座桥。
(五)表示状态的动词不能用于现在完成进行时。
I have known him for years. 我认识他已经好几年了。
* I have been knowing... 这类不能用于现在完成进行时的动词还有:love爱,like喜欢,
hate讨厌,等。
其构成形式如下: I / we / they have He / she / it has been + 动词的现在分词
功用如下:
1) 表示一个在过去开始而在最近刚刚结束的行动,如:
Ann is very tired. She has been working hard.
Why are you clothes so dirty? What have you been doing?
2) 表示一个从过去开始但仍在进行的行动,如:
It has been raining for two hours. (现在还在下)
Jack hasn’t been feeling very well recently.
3) 表示一个从过去开始延续到现在,可以包括现在在内的一个阶段内,重复发生的行动,如: She has been playing tennis since she was eight.
4) 现在完成时强调动作行为的结果、影响,而现在完成进行时只强调动作行为本身,如:
Tom’s hands are very dirty. He has been repairing the car.
注意: 现在完成时有否定结构、而现在完成进行时没有否定结构。
现在完成时态可表示做完的时期以及已有的经验、但现在完成进行时不可以
现在完成进行时的否定结构
在当代英语中,现在完成进行时有时也可用否定结构。如:
Since that unfortunate accident last week, I haven’t been sleeping at all well. 自从上周发生了那次不幸事故之后,我一直睡得很不好.
He hasn’t been working for me and I haven’t has that much contact with him. 他并没有给我工作过,我和他没有过那许多接触。
1. — I’m sure Andrew will win the first prize in the final.
— I think so. He ________ for it for months. (2008江苏)
A. is preparing B. was preparing C. had been preparing D. has been preparing
2. By the time he realizes he _________ into a trap, it’ll be too late for him to do anything about it. (2008山东)
A. walks B. walked C. has walked D. had walked
3. So far this year we _______ a fall in house prices by between 5 and 10 percent. (2008福建)
A. saw B. see C. had seen D. have seen
4. Cathy is taking notes of the grammatical rules in class at Sunshine School, where she ______ English for a year. (2007湖南)
A. studies B. studied C. is studying D. has been studying
5. Danny _________ hard for long to realize his dream and now he is popular. (2007福建)
A. works B. is working C. has worked D. had worked
6. —I have got a headache.
—No wonder. You_________ in front of that computer too long. (2007江西)
A. work B. are working C. have been working D. worked
7. The unemployment rate in this district_______ from 6% to 5% in the past two years. (2007上海)
A. has fallen B. had fallen C. is falling D. was falling
8. Now that she is out of job, Lucy ___ going back to school,but she hasn’t decided yet.(北京)
A. had considered B. has been considering
C. considered D. is going to consider
9. —______ you ______ him around the museum yet? (2007江苏)
—Yes. We had a great time there.
A. Have ; shown B. Do ; show C. Had; shown D. Did; show
10. —Hi, Tracy,you look pale.
—I am tired. I _______ the living room all day.
A. painted B. had painted C. have been painting D. have painted
1-5 DCDDC 6-10 CABAC
14、15、16过完进、将完进和过将进比较冷门不需要掌握
时态与时间状语
一般现在时 every …, sometimes, at …, on Sunday,
一般过去时 yesterday, last week, an hour ago, the other day, in 1982, just now
一般将来时 next…, tomorrow, in+时间,
现在完成时 for, since, so far, ever, never, just, yet, till/until, up to now, in past years, always, recently
过去完成时 before, by, until, when, after, once, as soon as
过去进行时 this morning, the whole morning, all day, yesterday, from nine to ten last evening… when, while
将来进行时 soon, tomorrow, this evening, on Sunday, by this time, tomorrow, in two days, tomorrow evening
练习1
1.(2002全国高考题)—You haven’t said a word about my new coat,Brenda.Do you like it?
—I’m sorry I ________ anything about it sooner.I certainly think it’s pretty on you.
A.wasn’t saying B.don’t say C.won’t say D.didn’t say
2.(2002全国高考题)I wonder why Jenny ________us recently.We should have heard from her by now.
A.hasn’t written B.doesn’t write C.won’t write D.hadn’t written
3.(2003北京春季高考题)—When will you come to see me,Dad?
—I will go to see you when you ________ the training course.
A.will have finished B.will finish C.are finishing D.finish
4.(2003北京春季高考题)—How long ________ at this job?
—Since 1990.
A.were you employed B.have you been employed
C.had you been employed D.will you be employed
5.(2003上海春季高考题)By the end of last year,another new gymnasium ________ in Beijing.
A.would be completed B.was being completed
C.has been completed D.had been completed
6.(2002北京高考题)The little girl ________her heart out because she ________ her toy bear and believed she wasn’t ever going to find it.
A.had cried; lost B.cried; had lost
C.has cried; has lost D.cries; has lost
7.(2002北京高考题)—Excuse me,sir.Would you do me a favor?
—Of course.What is it?
—I ________ if you could tell me how to fill out this form.
A.had wondered B.was wondering
C.would wonder D.did wonder
8.(2002上海高考题)He will have learned English for eight years by the time he ________ from the university next year.
A.will graduate B.will have graduated
C.graduates D.is to graduate
9.(2002上海高考题)I feel it is your husband who ________for the spoiled child.
A.is to blame B.is going to blame
C.is to be blame D.should blame
10.He has been writing the composition the whole morning and he still ________.
A.has been B.does C.has D.is
11.If city noises ________ from increasing,people ________ shout to be heard even at the dinner table 20 years from now.
A.are not kept; will have to B.are not kept; have to
C.do not keep; will have to D.do not keep; have to
12.The price ________,but I doubt whether it will remain so.
A.went down B.will go down
C.has gone down D.was going down
13.—How long ________ each other before they ________ married?
—For about a
year.
A.have they known; get B.did they know; get
C.do they know; are going to get D.had they known; got
14.You can’t move in right now.The house ________.
A.has painted B.is painted C.is being painted D.is painting
15.—Hey,look where you are going!
—Oh,I’m terribly sorry.________.
A.I’m not noticing B.I wasn’t noticing
C.I haven’t noticed D.I don’t notice
16.The reporter said that the UFO ______ east to west when he saw it.
A.was traveling B.traveled C.had been traveling D.was to travel
17.—Is this raincoat yours?
—No,mine ________ there behind the door.
A.is hanging B.has hang C.hangs D.hang
18.I turned around and saw everybody ________ at a man who ________ loudly in a foreign language.
A.was staring; was shouting B.was staring; shouting
C.staring; shouting D.stared; shouted
19.Henry remained silent for a moment.He ________.
A.thought B.had thought C.was thinking D.was thought
20.We would like to go and thank him ourselves,but we ________ out his address yet,
A.haven’t found B.hadn’t found C.didn’t find D.don’t find
21.Shirley ________ a book about China last year but I don’t know whether she has finished.
A.has written B.wrote C.had written D.was writing
22.—Have you got your test result?
—Not yet.The papers ________.
A.are not correcting B.have not corrected
C.are still being corrected D.have already been corrected
23.See the clouds! It ________ rain!
A.will B.is going to C.must D.certainly
24.Do I have to take this medicine? It ________ so terrible.
A.tastes B.is tasting C.is tasted D.has tasted
25.Don’t take the magazine away.It ________ me.
A.is belonged to B.belongs to
C.was belonged to D.is belonging to
26.Is this the third time that you ________ late?
A.have been B.am C.was D.had been
27.—Do you know when Tom ________ from abroad?
—Perhaps it will be a long time before he ________.
A.will come; will come B.comes; will come
C.will come; comes D.comes; comes
28.My uncle said that he would telephone but I _____from him so far.
A.didn’t hear B.hadn’t heard C.haven’t heard D.won’t hear
29.The telephone ________ four times in the last hour,and each time it ________ for my
roommate.
A.has rung; was B.has been ringing; is
C.had rung; was D.rang; has been
30.A storm ________ by a calm.
A.is often being followed B.was often followed
C.is often followed D.has often been followed
31.The pen I ________ I ________ is on my desk,right under my nose.
A.think; lost B.thought; had lost
C.think; had lost D.thought; lost
32.—We could have walked to the station.It was so near.
—Yes,a taxi ________ at all necessary.
A.wasn’t B.hadn’t been C.couldn’t be D.won’t be
33.A friend of mine returned to his house after a holiday only to find it ________.
A.to be broken B.had broken into
C.was broken D.had been broken into
34.They believed that by using computers the production of their factory ________.
A.will greatly increase B.would greatly increase
C.would be increased greatly D.will have been greatly increased
35.His eyes shone brightly when he finally received the magazines he ________.
A.had long been expected B.had long expected
C.has long expected D.was long expected
36.—Do you like the new pen?
—Yes,it ________ very well.
A.is written B.is writing C.writes D.wrote
37.—Oh,it’s you? I didn’t recognize you.
—I ________ my hair cut,and I ________ new glass.
A.had; was wearing B.have had; am wearing
C.had; wore D.have had; wear
38.As she ________ the newspaper,Granny ________ asleep.
A.read; was falling B.was reading; fell
C.was reading; was falling D.read; fell
39.However hard you _______,you will never succeed in pleasing her.
A.try B.will try C.should try D.would try
40.—Can I help you,sir?
—Yes,I bought this radio yesterday,but it ________.
A.didn’t work B.won’t work C.can’t work D.doesn’t work
41.—How are you today?
—Oh,I ________ as ill as I do now for a very long time.
A.didn’t feel B.wasn’t feeling C.don’t feel D.haven’t felt
42.When Jack arrived he learned Mary ________ for about an hour.
A.had gone B.had set off C.had left D.had been away
43.By this time tomorrow we ________ the machine.
A.have repaired B.shall have repaired
C.will repair D.would repair
44.I don’t think Jim saw me,he ________ into
space.
A.just stared B.was just staring
C.has just stared D.had just stared
45.Helen ________ her key in the office so she had to wait until her husband ________ home.
A.had left; came B.has left; comes
C.left; had come D.had left; would come
46.—You have left the light on.
—Oh,so I have.________ and turn it off.
A.I’ll go B.I’ve gone C.I go D.I’m going
47.This is Ted’s photo.We miss him a lot.He ________ trying to save a child in earthquake.
A.killed B.is killed C.was killed D.was killing
48.The notice ________ “No smoking.”
A.is wrote B.reads C.writes D.is read
49.Good care must ________ babies particularly while they are ill.
A.take B.take of C.be taken D.be taken of
50.Shortly after we ____,a waiter came over to our table with a smile.
A.seated B.were seated C.sat ourselves D.had seated
51.—You look pale,what troubled you?
—I ________ my dead friend.
A.am thinking about B.was thinking about
C.had thought about D.will think about
52.John and I ________ friends for eight years.We first got to know each other at a Christmas party.But we ________ each other a couple of times before that.
A.had been; have seen B.have been; have seen
C.have been; had seen D.had been; had seen
53.Do make sure that you ________ a seat today!
A.got B.get C.should D.have get
54.We ________ at the house as we ________ of buying it.
A.looked; were thinking B.were looking; were thinking
C.were looking; thought D.looked; had thought
55.—I’m told that you are leaving for Beijing.
—Who ________ so?
A.said B.had said C.says D.has said
56.I ________ the room to be empty but found it occupied.
A.had thought B.have thought C.didn’t think D.was thinking
57.Selecting a mobile phone for personal use is no easy task because technology ________ so rapidly.
A.will have changed B.has changed C.is changing D.will change
58.I ________ ping-pong quite well,but I haven’t had time to play since the new year.
A.will play B.have played C.played D.play
59.Visitors ________ not to touch the exhibits.
A.will request B.are requested C.are requesting D.request
60.They ________ a snowstorm on their way home.
A.caught in B.had caught
C.were caught D.were caught in
练习2
1. --- Oh, dear. I forgot the air tickets.
--- You ______ something.
A. have left B. are always leaving
C. are leaving D. always left
2. --- I ______ so busily recently that I ______ no time to help you with your math.
--- That’s OK. I can manage it by myself.
A. have been working; have
B. have worked; had
C. am working; will have
D. had been working; had had
3. Remember to send me a photo of us next time you ______ to me.
A. are writing B. will write
C. has written D. write
4. He ______ at the meeting, but his heart attack prevented him.
A. will speak B. is going to speak
C. had to speak D. was going to speak
5. --- I beg your pardon, but I didn’t quite catch you.
--- Oh, I ______ myself.
A. am talking to B. talked about
C. have talked to D. was talking to
6. I ______ ping-pong quite well, but I haven’t had time to play since the New Year.
A. will play B. have played
C. played D. play
7. I first met Tom 10 years ago. He ______ in a radio factory at that time.
A. had worked B. has worked
C. was working D. has been working
8. --- What ______ when I phoned you?
--- I ______ my work, and I wanted to go out.
A. have you done; finished
B. were you doing; have finished
C. did you do; had just finished
D. were you doing; had just finished
9. --- Have you finished the report?
--- No. I ______ it all this week.
A. will do B. had done
C. have done D. have been doing
10. I can guess you were in a hurry. You ______ your sweater inside out.
A. had worn B. wore
C. were wearing D. are wearing
11. --- We ______ that you would fix the TV set this week.
--- I’m sorry. I ______ to fix it this week, but I’ve been too busy.
A. had expected; had intended
B. are expecting; had intended
C. expect; intend
D. expected; intend
12. --- Why? Tom, your shirt is so dirty!
--- Mum, I ______ my storeroom downstairs.
A. cleaned B. have cleaned
C. was cleaning D. have been cleaning
13. They won’t buy new clothes because they ______ money to buy a new house.
A. save B. are saving
C. have saved D. were saving
14. The traffic in our city is already good and it ______ even better.
A. gets B. got C. has got D. is getting
15. --- I will come to attend your lecture at 10:00 tomorrow.
--- I’m sorry, by then my lecture will have ended and I ______ my guests in my office.
A. is being met B. will meet
C. will be meeting D. will have met
16. --- Alice came back home the day before yesterday.
--- Really? Where ______?
A. has she been B. had she been
C. has she gone D. had she gone
17. I know Mr. Brown; we ______ to each other at an international conference.
A. are introduced B. are been introduced
C. were introduced D. had been introduced
18. --- Where do you think ______ he ______ the computer?
--- Sorry. I have no idea.
A. has; bought B. 不填; bought
C. did; buy D. 不填; buys
19. Don’t bother to look for my dictionary --- it ______ some day.
A. turns up B. has turned up
C. will turn up D. is going to turn up
20. --- What do you think of this kind of TV set, which ______ in Shanghai?
--- Well, I don’t care about such things.
A. was made B. is made
C. has been made D. had been made
21. --- Did he notice you enter the room?
--- I don’t think so. He ______ to the radio with his eyes shut.
A. listened B. was listening
C. has listened D. had listened
22. The plane ______ at 7:00 pm, so I have to be at the airport by 6:40 at the latest.
A. has left B. would leave
C. will have left D. leaves
23. The train ___ at the present speed until it reaches the foot of the mountain at about nine o’clock tonight.
A. went B. is going C. goes D. will be going
24. I used to drink a lot of tea but these days I ______ coffee.
A. prefer B. preferred
C. had preferred D. am preferring
25. The vegetables didn’t taste very good. They ______ too long.
A. had been cooked B. were cooked
C. have cooked D. cooked
26. --- Remember the first time we met, Jim?
--- Of course I do. You ______ in the library.
A. were reading B. had read
C. have read D. read
27. I want to buy that kind of cloth because I ______ the cloth ______ well.
A. have told; washes
B. have been told; washes
C. was told; washed
D. have been told; is washed
28. --- Is Tom still smoking?
--- No. By next Saturday he ______ for a whole month without smoking a single cigarette.
A. will be B. will have gone
C. will have been D. has been going
29. --- ______ Betty this morning?
--- Not yet, but she is sure to be here before noon.
A. Have you seen B. Will you see
C. Do you see D. Did you see?
30. Jim talked for about half an hour yesterday. Never ______ him talk so much.
A. I heard B. did I hear
C. I had heard D. had I heard
31. --- Look at the black clouds. It ______ soon.
--- Sure. If only we ______ out.
A. is raining; didn’t come
B. is to rain; won’t start
C. will rain; haven’t started
D. is going to rain; hadn’t come
32. He ___ articles for our wall-newspaper these three years, and he ____ about forty articles.
A. has been writing; has written
B. has been writing; wrote
C. is writing; has been writing
D. has written; has written
33. She ______ to the office than she got down to writing the report.
A. has no sooner got B. had hardly got
C. no sooner got D. had no sooner got
34. When he was alive, the old scientist used to say that knowledge ______ from practice and he gained his experience by doing a lot of practical work.
A. was coming B. had come
C. comes D. would come
35. --- Don’t forget to bring my new books tomorrow afternoon.
--- No, I ______.
A. don’t B. do C. won’t D. will
36. I decided to go to the library as soon as I ______.
A. finished what I was doing
B. finished what I did
C. would finish what I was doing
D. finish what I did
37. You won’t know whether the coat fits you until you ______ it on.
A. will try B. have tried
C. tried D. are trying
38. My dictionary ______. I have looked for it everywhere but still ______it.
A. has lost; don’t find
B. is missing; don’t find
C. has lost; haven’t found
D. is missing; haven’t found
39. ______ it with me and I’ll see what I can do.
A. When left B. Leaving
C. If you leave D. Leave
40. --- How are you planning to travel to Shanghai?
--- I ______ yet, but I ______ taking a train.
A. didn’t decide; am considering
B. haven’t decided; consider
C. haven’t decided; am considering
D. hadn’t decided; have considered
41. --- Excuse me, sir. Would you do me a favour?
--- Of course. What is it?
--- I ______ if you could take me to the station.
A. would wonder B. did wonder
C. was wondering D. had wondered
42. --- Got your driving license?
--- No. I ______ too busy to have enough practice, so I didn’t take the driving test last week. I’m going to next week.
A. was B. have been C. am D. had been
43. With the development of science, more new technology ______ to the field of IT.
A. has introduced B. is being introduced
C. is introduced D. was introduced
44. --- Who’s the man over there?
--- It’s Jack.
--- Oh? ______ in Italy.
A. I think he’s
B. I’ve thought he’s been
C. I thought he was
D. I’d thought he’d been
45. --- I dropped in at your house at about ten last night, but you weren’t in.
--- I ______ regular exercises at the club.
A. did B. was doing C. had done D. have been doing
46. --- Each of the students, working hard at their lessons, ______ the book.
--- So have I.
A. is reading B. has read C. reading D. reads
47. The baby is generally healthy, but every now and then he ______ a cold.
A. has caught B. is catching
C. will catch D. does catch
48. It is when the plane ______ that you’d better find out at the booking office.
A. would take off B. had taken off
C. was taking off D. is taking off
49. --- I’m sorry, but there’s no smoking on this flight.
--- Oh, I ______ that. Sorry, I won’t again.
A. don’t know B. didn’t know
C. won’t know D. haven’t known
50. I thought Jim would say something about his school report, but he ______ it.
A. doesn’t mention B. hadn’t mentioned
C. didn’t mention D. hasn’t mentioned
答案:
1-5 BADDD 6-10 DCDDD 11-15 ADBDC 16-20 BCBCB
21-25 BDDAA 26-30 ABBAD 31-35 DADCC 36-40 ABDDC
41-45 CDBCB 46-50 BDDBC