- 1.69 MB
- 2021-10-12 发布
- 1、本文档由用户上传,淘文库整理发布,可阅读全部内容。
- 2、本文档内容版权归属内容提供方,所产生的收益全部归内容提供方所有。如果您对本文有版权争议,请立即联系网站客服。
- 3、本文档由用户上传,本站不保证质量和数量令人满意,可能有诸多瑕疵,付费之前,请仔细阅读内容确认后进行付费下载。
- 网站客服QQ:403074932
Grammar
Tenses
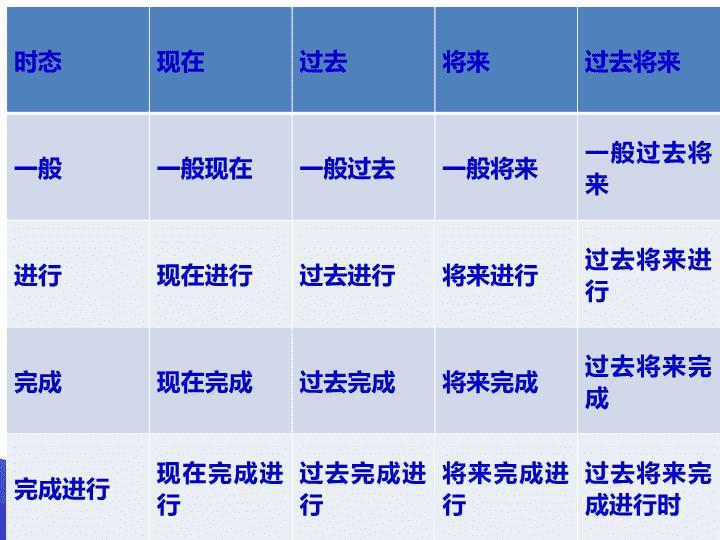
时态
现在
过去
将来
过去将来
一般
一般现在
一般过去
一般将来
一般过去将来
进行
现在进行
过去进行
将来进行
过去将来进行
完成
现在完成
过去完成
将来完成
过去将来完成
完成进行
现在完成进行
过去完成进行
将来完成进行
过去将来完成进行时
一般现在时
(1)构成
一般 现在时主要用动词原形表示,如果主语是第三人称单数,在动词原形后加
-s
或
-es
Tom often helps his parents do housework at home.
Sometimes Lucy washes her clothes herself.
(
2)
一般现在时的用法
1)
表经常性或习惯性的动作或存在的状态。
He often goes to school by bike.
2)
表客观事实或普遍真理。
The earth goes around the sun
.
3)在含时间和条件状语从句的复合句中如由
when, if, as soon as,before, until,once, the moment
等,用一般现在表将来,即主将从现。
The moment he arrives, I
’
ll tell him about it .
I will go with you as soon as I finish my work.
4
)在某些以
here
,
there
开头的句子中用一般现在时表正在发生的动作。
There goes the bell.
(5)
与一般现在时连用的时间状语
表频度的副词,
always, often, usually, sometimes
等。
On Sundays, on Monday afternoon , every day, every morning, every year
Once a year, twice a month, three times a week
一般过去时
(
1
)构成:用动词的过去式表示。
Last week Tom made a model plane with his friend Jack.
(2)
一般过去时的用法
1
)表过去某时间发生的动作或存在的状态
We visited the factory last week.
2
)表示在过去一段时间内,经常性或习惯性的动作。
When I was a child, I often played football in the street.
He always went to work by bus.
3
)和一般过去时连用的时间状语
last night, yesterday, last week, some years ago, in 1995, in the past, the other day, at that time, just now.
3.
一般将来时
(
1
)表将来发生的动作或存在的状态。
构成:
be going to + v.
原
will + v.
原
shall + v.
原
1
. be going to +v.原,表示将来
。
计划打算做某事。
I'm going to buy a new coat this winter.
b
. 有迹象要发生的事
Look at those black clouds. It is going to rain.
2
. shall
一般用于第一人称(we,I),表建议
Shall we go swimming tomorrow?
3. will
表有礼貌的询问对方是否愿意或表客气的邀请或命令
。
Will you please lend me your bike?
还可表单纯的将来,与人的主观愿望无关。
The sun will rise at 6: 30 tomorrow morning.
4. be doing
表示将来
常用这种结构的动词有
go, come, leave, stay, start , begin
等。
表即将发生或安排好要做的事。
We are leaving for London.
I am coming soon.
5. be about to+ v.
原
be to+ v.
原, 都表将来
, “
马上做某事”
The train is about to start.
She is to be married next month.
现在进行时
表此时此刻正在进行的动作。
通常由表示“此刻”的时间状语(now, at this moment),
或通过Look/Listen!这两个提示语来表明此时此刻动作正在进行。
Listen, she is singing a song.
2.现阶段正在进行的动作或存在的状态。
They are studying hard this term.
3. go, leave, arrive, return, start, begin
用现在进行表将来。
I am going to Beijng this Sunday.
现在进行时的特殊用法
现在进行时往往与constantly, always, forever continually, all the time等状语连用,
表示一种反复出现或习惯性的动作,带有“厌恶”、“赞叹”等感情色彩
She's constantly complaining. 。
He is forever thinking of doing more for the students.
现在完成时
构成形式:主+ has/ have +done
常被称为“与现在有联系的过去”,因此它不能与明确的过去时间状语连用。
(1)现在完成时表示过去发生或已完成的动作对现在造成的影响.
The temperature has increased by 10℃.
(结果:It is quite hot now.)
Air pollution has taken the lives of many people.
(结果:Air pollution is very serious now.)
-----Have you found your lost pen yet?
----- No, I haven’t found it yet.
2)现在完成时表示过去已经开始,持续到现在.
(还有可能持续下去)常与
for +
时间段
,
since+
时间点
连用, 多为延续性动词。
We have lived here since 2000.
I haven’t watched TV for two weeks.
句型:(1) 主语+have done +since句(过去时)
We have lived here since 2000.
My aunt has taught English since she came to the school.
(2) It is/ has been + 一段时间+ since从句(过去时)
It is five years since he joined the army.
(3) This/ It is the first/ second...time +that从句
This is the first time that I have come here.
几个副词在现在完成时的用法
1
)
just “
刚刚” ,常放在助动词与过去分词之间。
He has just come back from Beijing.
2)
e
ver “
曾经“ , 用疑问句或否定句中,常放在助动词与过去分词之间。
Have you ever been to Shanghai .
3)
n
ever “
从来没有”, 常与
before
连用,常放在助动词与过去分词之间。
I have never traveled by plane before.
4)
b
efore “
以前“,总放在句末,不受句型限制。
I haven’t heard of it before.
5)
a
lready “
已经” 用于肯定句,常放在助动词与过去分词之间,也可放句末。
I have already finished my homework.
6
)
yet
用疑问句中意为“已经”
,
用否定句中表“还”, 常放句末。
She has not gone to bed yet.
延续性和非延续动词用法
我离开学校已经八年了
。
误:
I’ve left this school for eight years
.
正:
I’ve been away from this school for eight years.
他借用我的词典已两天了
。
误:
He has borrowed my dictionary for two days.
正:
He has kept my dictionary for two days.
非延续动词
延续动词
buy borrow
have ; keep
die finish
be dead; be over
open go
be open; be there
join leave
be in ; be away
put on wake up
wear; be awake
catch a cold fall asleep
have a cold be asleep
arrive/ reach
be
过去完成时
(1)一件事情发生在过去,而另一件事先于它发生(表“过去的过去”)发生在前的事情的动词用过去完成
。
I had learnt 5000 words before I entered the university.
Before he slept, he had worked for 12 hours
.
(2)表示从过去某一时间开始,一直延续到过去的另一时间的动作,常用的时间状语有:until/ by/ before/ by the end of +“表过去的某一时间”。
By the end of last year we had built five new houses.
(
3
)在
told, said, knew, heard, thought
等动词后的宾语从句。
She said (that) she had never been to Paris
.
(4)表示意向的动词,如hope, wish, expect, think, intend, mean, suppose等,用过去完成时表示"原本…,未能…“
We had hoped that you would come, but you didn't.
返回
一般过去时与现在完成时之比较
1
)
一般
过去时
是一种过去时态,侧重于表示过去的动作,与现在无关,
强调动作;
现在完成时
是与现在有关的时态,属现在时态范畴;
强调过去的事情对现在的影响,强调的是影响。
请大家认真分析比较下列各例句:
I saw this film yesterday.
(强调看的动作发生过了。)
I have seen this film.
强调对现在的影响,电影的内容已经知道了。
2
)连用的时间状语不同:与现完:
already, yet, still, just, so far, in the last/ past
(
years…), before, ever, never, since, for
等。
◎ 一般过去时的时间状语有:
yesterday, last week
,
…ago, in1980, in October, just now
等。
Father bought that watch ten years ago.
Have you ever picked flowers in the park?
知识扩展:不用进行时的动词
1)
事实状态的动词。
如:
have, belong, possess, cost, owe, exist, include, contain, matter, weigh, measure, continue
I have two brothers.
This house belongs to my sister.
2)
心理状态的动词。
如:
know, realize, think see, believe, suppose, imagine, agree, recognize, remember, want, need, forget, prefer, mean, understand, love, hate
I need your help.
He loves her very much.
3)
瞬间动词。
如:
accept, receive, complete, finish, give, allow, decide, refuse.
I accept your advice.
4)
系动词。
如:
seem, remain, lie, see, hear, smell, feel, taste, get, become, turn
You seem a little tired.
返回
过去进行时
形式:主+were /was +doing
过去进行时的主要用法: 表示过去某一时刻正在进行的动作
常用的时间状语有:
this morning, the whole morning,
all day yesterday, from nine to ten last evening
My brother fell while he
was riding
his bicycle and hurt himself.
It
was raining
when they left the station.
When I got to the top of the mountain, the sun
was shining.
Mary ___ a dress when she cut her finger.
A. made B. is making
C. was making D. makes
2) As she ___ the newspaper,
Granny ___ asleep.
read; was falling
was reading; fell
C. was reading; was falling
D. read; fell
答案
B.
句中的
as = when, while
,意为
"
当
……
之时
"
。
句意为
"
在她看报纸时,奶奶睡着了。
"
句中的
fell (fall
的过去时
)
,是系动词,后跟形容词,如:
fall sick
。
返回
过去将来时
(
1
) 从过去某一段时间看将来发生的动作或存在的状态,常用于宾从中,谓语由“
would+v.
原”。
He said he would buy some fruit for his sister.
He asked when the meeting would end.
(2)
表示曾经打算或准备要做的动作;或表有某种要发生某事。
用
were/was going to + v.
原
.
I thought it was going to rain soon.
They were going to start a new job when I saw them then.
(3) go, come, leave, arrive, start
用过去进行时表过去按计划即将发生的事。
He said he was coming this evening
.
2
. have been to ,have gone to
与
have been in
三种结构的区别
have been to
过去曾经去过某地,现已回来
have gone to
已去了某地,现在还没回来
have been in
已在某地(待了多久)
该地小地点用
at,
大地点用
in
。
1.
吉姆已和他的家人去了伦敦。
Jim ___________ London with his family.
2.
你以前过去北京吗?
Have you ___________ Beijing before?
3.
格林一家在中国已两年了。
The Greens __________China for two years.
4.
王老师已在这个学校十年了。
Mr. Wang ____________ this school for ten years.