- 13.32 KB
- 2021-05-20 发布
- 1、本文档由用户上传,淘文库整理发布,可阅读全部内容。
- 2、本文档内容版权归属内容提供方,所产生的收益全部归内容提供方所有。如果您对本文有版权争议,请立即联系网站客服。
- 3、本文档由用户上传,本站不保证质量和数量令人满意,可能有诸多瑕疵,付费之前,请仔细阅读内容确认后进行付费下载。
- 网站客服QQ:403074932
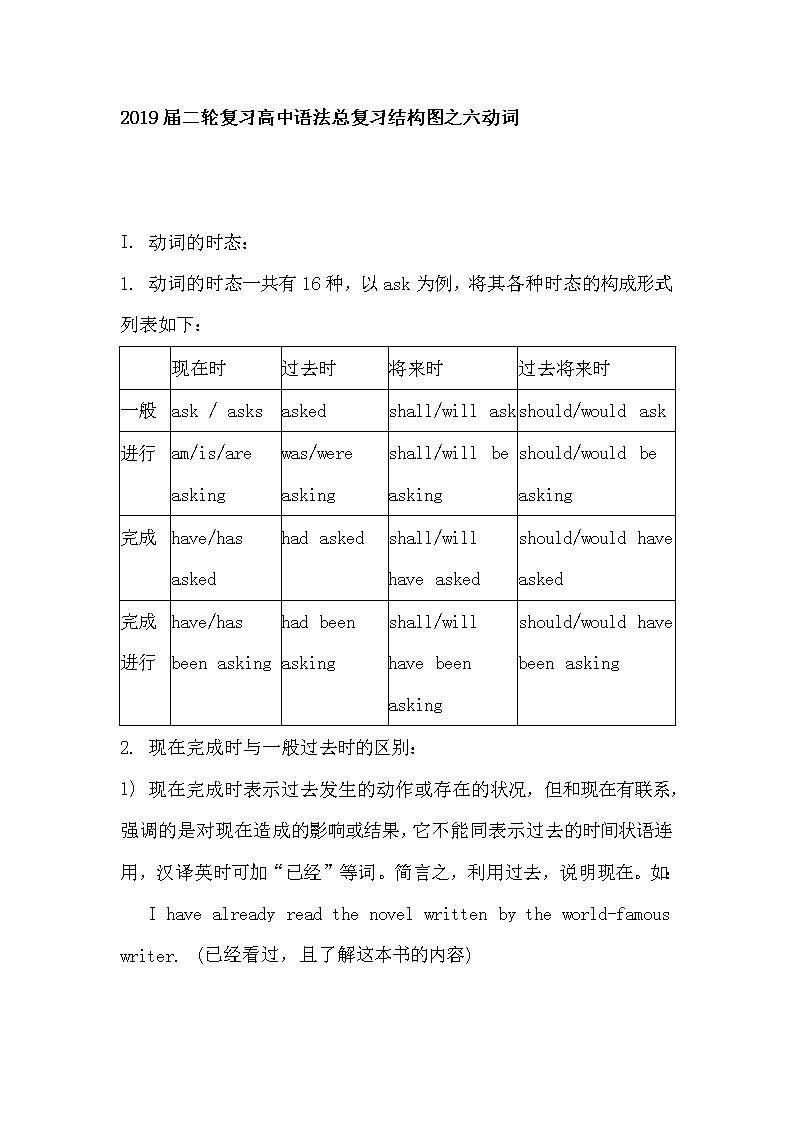
2019届二轮复习高中语法总复习结构图之六动词
I. 动词的时态:
1. 动词的时态一共有16种,以ask为例,将其各种时态的构成形式列表如下:
现在时
过去时
将来时
过去将来时
一般
ask / asks
asked
shall/will ask
should/would ask
进行
am/is/are asking
was/were asking
shall/will be asking
should/would be asking
完成
have/has asked
had asked
shall/will have asked
should/would have asked
完成进行
have/has been asking
had been asking
shall/will have been asking
should/would have been asking
2. 现在完成时与一般过去时的区别:
1) 现在完成时表示过去发生的动作或存在的状况,但和现在有联系,强调的是对现在造成的影响或结果,它不能同表示过去的时间状语连用,汉译英时可加“已经”等词。简言之,利用过去,说明现在。如:
I have already read the novel written by the world-famous writer. (已经看过,且了解这本书的内容)
2) 一般过去时只表示过去发生的动作或状态,和现在无关,它可和表示过去的时间状语连用,汉译英时可加“过”,“了”等词。简言之,仅谈过去,不关现在。如:
①I read the novel last month. (只说明上个月看了,不涉及现在是否记住)
②I lived in Beijing for ten years.(只说明在北京住过十年,与现在无关)
3. 现在完成时与现在完成进行时的区别:
两者都可以表示“从过去开始一直持续到现在”,在含义上如着重表示动作的结果时,多用现在完成时,如着重表示动作一直在进行,即动作的延续性时,则多用现在完成进行时。一般不能用于进行时的动词也不能用于现在完成进行时。
①I have read that book.我读过那本书了。 ②I have been reading that book all the morning. 我早上一直在读那本书。
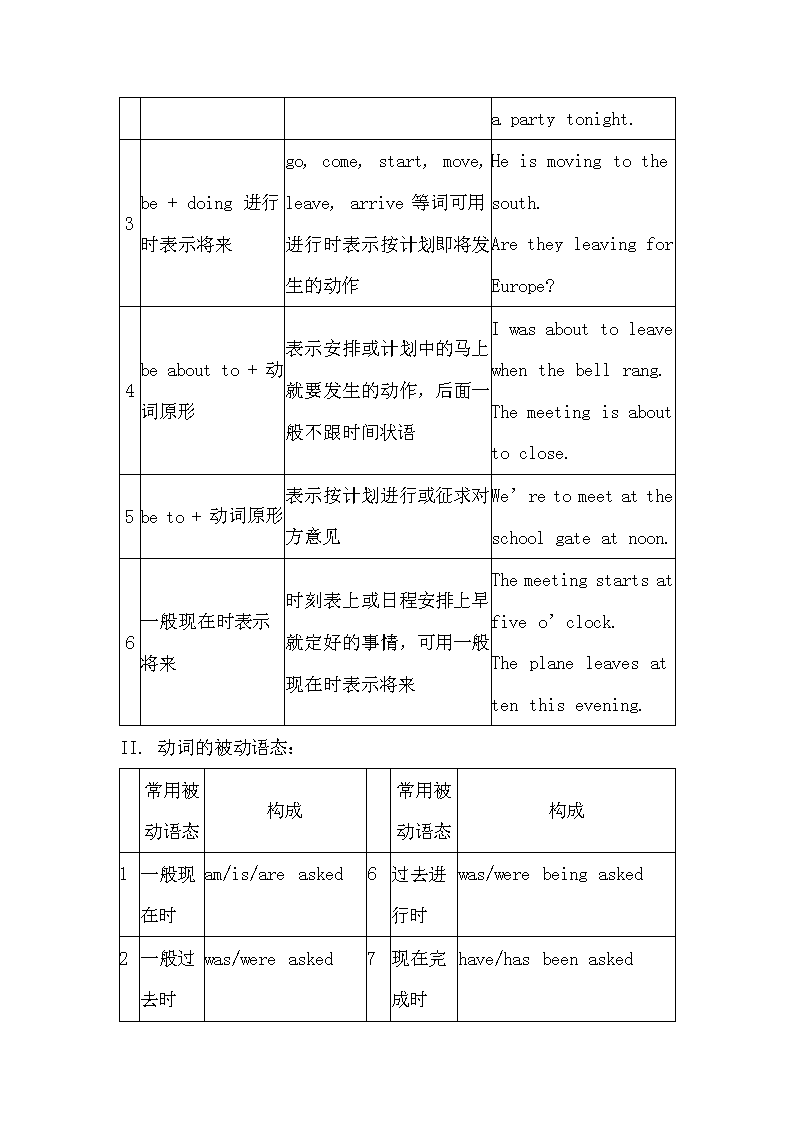
4. 一般将来时的表达方式:
将来时
用法
例句
1
will/shall+动词原形
表示将来发生的动作或存在的状态
My sister will be ten next year.
2
be going to+动词原形
含有“打算,计划,即将”做某事,或表示很有可能要发生某事
It’s going to clear up.
We’re going to have
a party tonight.
3
be + doing 进行时表示将来
go, come, start, move, leave, arrive等词可用进行时表示按计划即将发生的动作
He is moving to the south.
Are they leaving for Europe?
4
be about to + 动词原形
表示安排或计划中的马上就要发生的动作,后面一般不跟时间状语
I was about to leave when the bell rang.
The meeting is about to close.
5
be to + 动词原形
表示按计划进行或征求对方意见
We’re to meet at the school gate at noon.
6
一般现在时表示将来
时刻表上或日程安排上早就定好的事情,可用一般现在时表示将来
The meeting starts at five o’clock.
The plane leaves at ten this evening.
II. 动词的被动语态:
常用被动语态
构成
常用被动语态
构成
1
一般现在时
am/is/are asked
6
过去进行时
was/were being asked
2
一般过去时
was/were asked
7
现在完成时
have/has been asked
3
一般将来时
shall/will be asked
8
过去完成时
had been asked
4
过去将来时
should/would be asked
9
将来完成时
will/would have been asked
5
现在进行时
am/is/are being asked
10
含有情态动词的
can/must/may be asked
注
意
事
项
被动语态的否定式是在第一个助动词或情态动词后加not,短语动词的被动态不可漏掉其中介副词。固定结构be
going to, used to, have to, had better变为被动态时,只需将其后的动词变为被动态。 如:
Trees should not be planted in summer. / The boy was made fun of by his classmates.
Newspapers used to be sent here by the little girl.
汉语有一类句子不出现主语,在英语中一般可用被动结构表示。如:
It is believed that… It is generally considered that… It is said that…
It is well known that… It must be pointed out that… It is supposed that…
It is reported that… It must be admitted that… It is hoped that…
下面主动形式常表示被动意义:如:
The window wants/needs/requires repairing. The book is worth reading twice.
The door won’t shut. / The play won’t act. The clothes washes well. / The book sells well.
The dish tastes delicious. / Water feels very cold.
下面词或短语没有被动态:
leave, enter, reach, become, benefit, cost, equal, contain, last, lack, fit, fail, have, appear, happen, occur, belong to, take place, break out, come about, agree with, keep up with, consist of, have on, lose heart等等
相关文档
- 【英语】2019届高考英语二轮复习语2021-05-207页
- 2019届高考英语二轮复习专题增分技2021-05-2014页
- 高考英语二轮复习与策略专题限时集2021-05-205页
- 高考英语二轮复习与增分策略考前特2021-05-2018页
- 2019年高考英语二轮复习精编课件:短2021-05-2051页
- 高考英语二轮复习语言运用组合练12021-05-205页
- 【英语】2019届高考英语二轮复习考2021-05-208页
- 【英语】2019届高考英语二轮复习增2021-05-2022页
- 高考英语二轮复习Ⅱ卷强化增分练72021-05-206页
- 2019届高考英语二轮复习习题讲评课2021-05-2040页